主要摘自 Mastering Bitcoin - chapter07
区块链是一串使用密码学方法相关联产生的数据块。每一个区块都有一个唯一的哈希值,区块头还有一个指向前一个区块。每个区块只能有一个父区块,但可以暂时拥有多个子区块。
当父区块有任何改动时,父区块的哈希值也随之变化,因此子区块的「父区块哈希值」也改变,从而又将导致子区块的哈希值发生改变。以此类推,一旦一个区块有很多代以后,这种瀑布效应将保证该区块不会被改变,除非强制重新计算该区块所有后续的区块。而重新计算需要耗费巨大的计算量,所以一个长区块链的存在可以让区块链的历史不可改变。
Structure of a Block
| Size | Field (low) | Desciption (high) |
| 4 bytes | Block Size | The size of the block, in bytes, following this field |
| 80 bytes | Block Header | Several fields form the block header |
| 1-9 bytes (VarInt) | Transaction Counter | How many transactions follow |
| Variable | Transactions | The transactions recorded in this block |
Block Header
| Size | Field (low) | Desciption (high) |
| 4 bytes | Version | A version number to track software/protocol upgrades |
| 32 bytes | Previous Block Hash | A reference to the hash of the previous (parent) block in the chain |
| 32 bytes | Merkle Root | A hash of the root of the merkle tree of this block’s transactions |
| 4 bytes | Timestamp | The approximate creation time of this block (seconds from Unix Epoch) |
| 4 bytes | Difficulty Target | The proof-of-work algorithm difficulty target for this block |
| 4 bytes | Nonce | A counter used for the proof-of-work algorithm |
Linking Blocks in the Blockchain
{
"size" : 43560,
"version" : 2,
"previousblockhash" :
"00000000000000027e7ba6fe7bad39faf3b5a83daed765f05f7d1b71a1632249",
"merkleroot" :
"5e049f4030e0ab2debb92378f53c0a6e09548aea083f3ab25e1d94ea1155e29d",
"time" : 1388185038,
"difficulty" : 1180923195.25802612,
"nonce" : 4215469401,
"tx" : [
"257e7497fb8bc68421eb2c7b699dbab234831600e7352f0d9e6522c7cf3f6c77",
... many more transactions omitted ...
"05cfd38f6ae6aa83674cc99e4d75a1458c165b7ab84725eda41d018a09176634"
]
}
Merkle tree
区块链中的每个区块都包含了产生于该区块的所有交易,且以 Merkle 树表示。
Merkle Tree 就是不断两两哈希,最后得到一整棵树的最后哈希值,也就是根节点, Merkle Root.
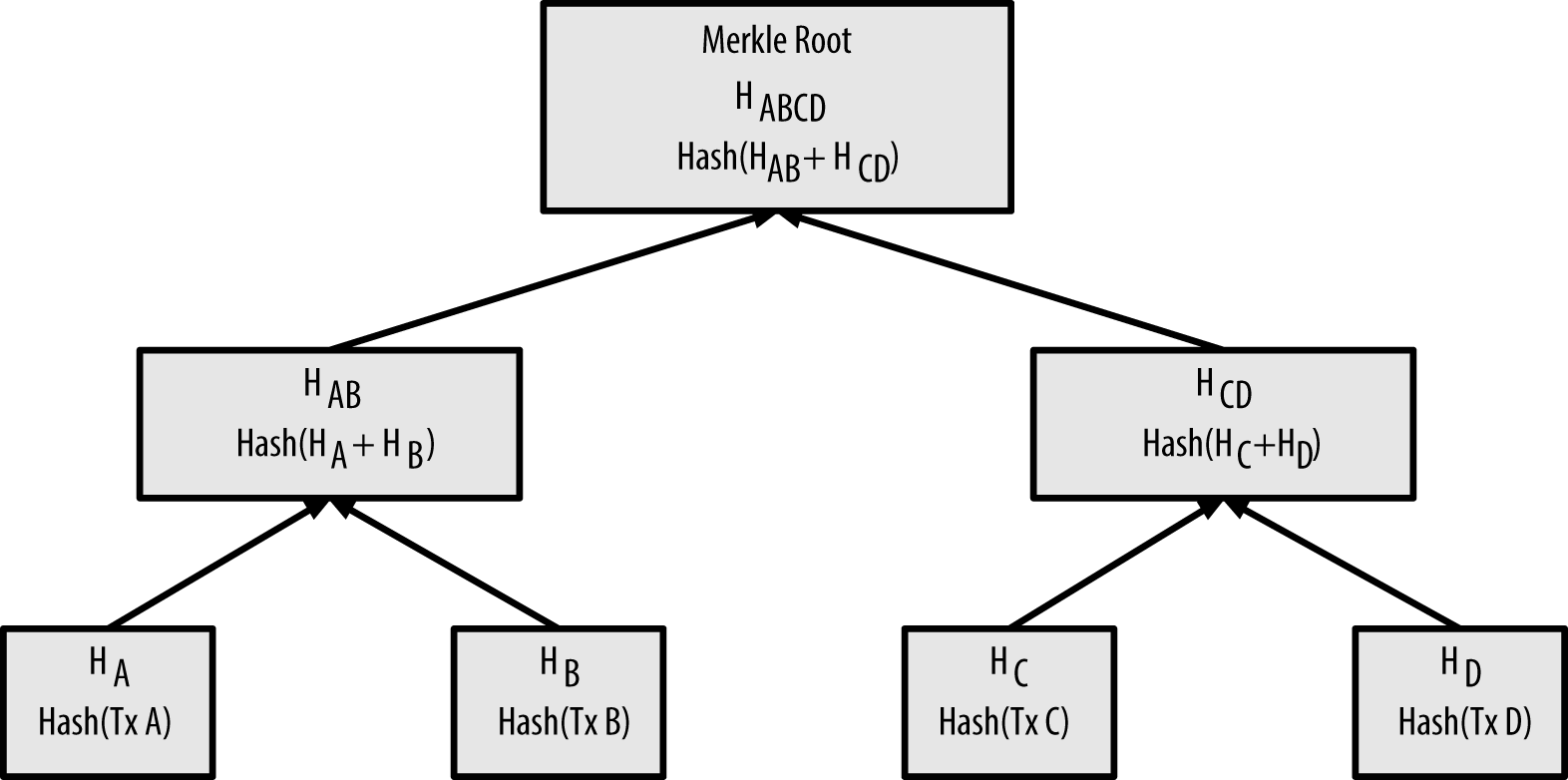
相比 Hash List, Merkle Tree 的一个好处是可以单独拿一个分支出来对部分数据进行校验,也能很容易就找到哪一小块数据是不对的。